Hey there, tech enthusiasts! Today, we’re taking you into the world of motherboards. The backbone of your computer – it’s the system allowing all the components to communicate with one another. They perform various functions which are difficult, but vital to understanding each of these functions. So, buckle up as we break down the several types of motherboards, and answer some of the burning questions you might have!
10 Different Types of Motherboards in India
Different Types of Motherboards in India
Motherboards come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each designed for specific use cases. Let’s explore the most common types of motherboards and what makes each one unique.
Advanced Technology (AT) Motherboard

The Advanced Technology (AT) motherboard was one of the first standard form factors in the personal computer world. Developed by IBM in the 1980s, It is essential to understand the evolution of motherboards. It typically has a large size, with a 12 x 13.8-inch dimension, and it introduced the 8-bit ISA slot. Although it’s mostly a relic today, it was a significant step that paved the way for more advanced motherboards.
Standard ATX Motherboard

The Standard ATX motherboard is widely used, Measuring 12 x 9.6 inches. These motherboards were introduced in 1995. These motherboards are the most versatile and compatible form factors that connect to different components. They are the first choice of professionals and gamers. The larger layout arranges multiple expansion ports and slots for its users.
Micro ATX Motherboard
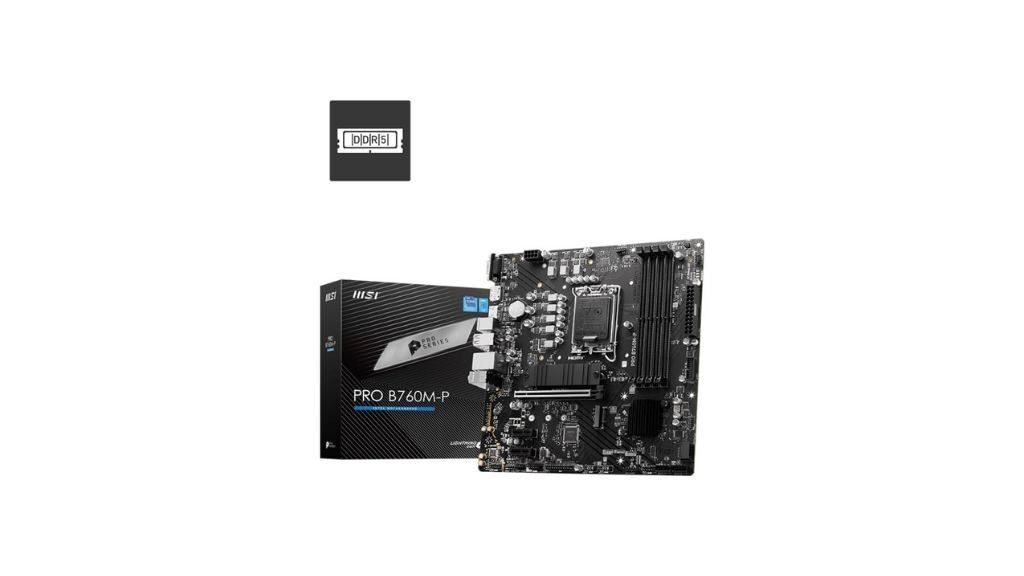

Micro ATX (mATX) motherboards are a version of the standard ATX motherboard, and their measurements are 9.6 x 9.6 inches. These motherboards are smaller comparatively. They enhance a great balance between cost, performance, and size. Micro ATX boards have fewer expansion slots than standard ATX motherboards however, they are budget-friendly. These Micro ATX (mATX) motherboards are awesome for office or home PCs.
eXtended ATX Motherboard
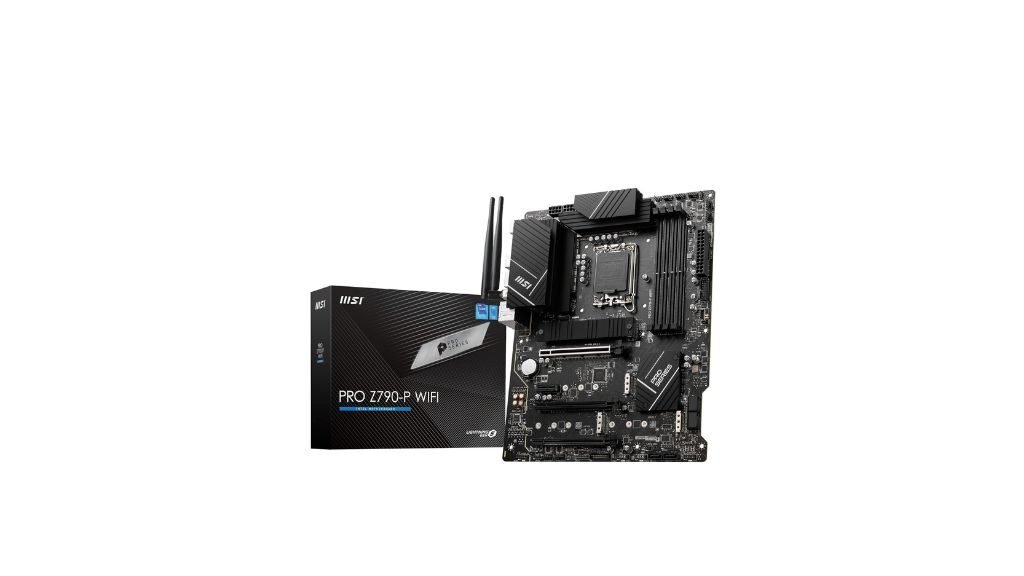

The eXtended ATX (E-ATX) motherboard is a larger variant of the standard ATX, measuring approximately 12 x 13 inches. It offers additional features that promise maximum and effective performance. It enables the highest configurability. They have a better power supply system that extends its capabilities. E-ATX motherboards are used in workstations, where extensive RAM configurations and multiple GPUs are necessary.
Flex ATX Motherboard
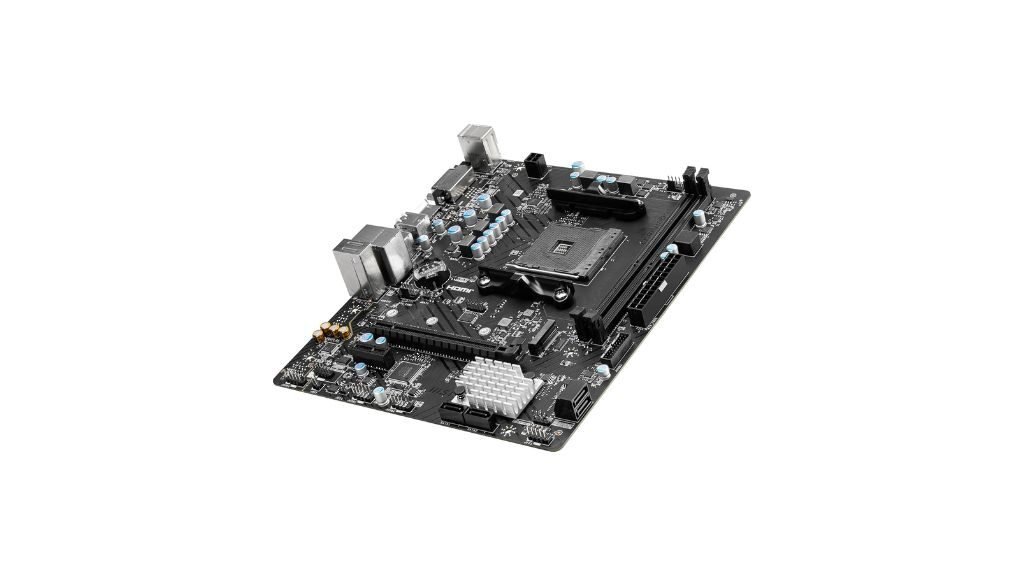

Flex ATX motherboards offer a unique blend of size and flexibility. Measuring 9 x 7.5 inches, they are designed for cases that require compact layouts while still maintaining a level of versatility. Flex ATX boards are often used in small form-factor PCs where space is at a premium but still allows room for customization and expansion. They support a range of components while optimizing space, making them a popular choice for home theater PCs or compact office setups.
Low-Profile Extended (LPX) Motherboard
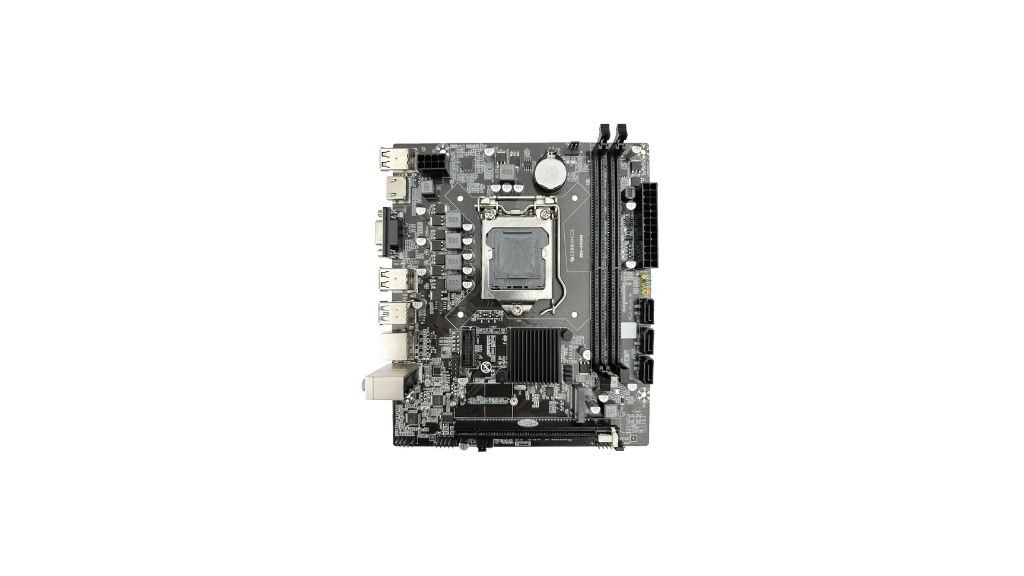

The LPX motherboard is another older form factor that emphasizes compact design. These boards are typically around 10.5 x 8 inches and were common in early desktop systems. LPX motherboards were designed to use a riser card for expansion slots, which saved space and allowed for a lower-profile case design. While you won’t find many modern systems utilizing LPX, it was critical for shaping smaller desktops.
BTX Motherboard

The Balanced Technology Extended (BTX) motherboard was developed in response to the cooling limitations of ATX motherboards. BTX boards feature a design that optimizes airflow and enhances cooling efficiency but haven’t been widely adopted. Measuring about 12.8 x 10.5 inches, they position components in a way that promotes better airflow, despite their relatively short-lived prominence. Some enthusiasts still enjoy their benefits in custom builds, but the ATX form has prevailed overall.
Pico BTX Motherboard

As an even more compact version of BTX, the Pico BTX motherboard measures about 10.4 x 8 inches. It’s designed for use in small form-factor PCs, particularly those that need to cater to mobile or energy-efficient computing needs. Like its larger BTX counterpart, Pico BTX focuses on improving airflow and cooling but in a size that’s ideal for ultra-compact systems. It’s great for portable builds but less common in today’s market.
Mini ITX Motherboard

The Mini ITX motherboard, measuring just 6.7 x 6.7 inches, has become extremely popular among PC builders who prioritize space and build aesthetics. Despite its small size, Mini ITX boards manage to pack in essential features and can support powerful components. These motherboards are ideal for gaming setups that require minimal footprints, server applications, or home theater setups. Their compact nature also promotes creativity in case design.
Mini STX Motherboard

The Mini STX motherboard is even smaller than Mini ITX, measuring around 5 x 5 inches. It’s designed for ultra-compact systems and mobile devices. Despite its size, Mini STX boards can still support full desktop CPUs and provide the necessary performance for lightweight tasks. If you’re looking to build a tiny powerhouse, these motherboards should be on your radar! They’re perfect for specialized applications such as digital signage or custom compact builds.
FAQs AboutTypes of Motherboards
What is a motherboard?
A motherboard is the main circuit board that allows all the parts of the computer to communicate with each other and get the work done. It is inside the computer and the central circuit board. It gathers the memory, CPU, and all the connectors to other computer hardware components.
What are the key features and components of a motherboard?
Key features and components of a motherboard include:
CPU socket
Memory slots (RAM)
Expansion slots (PCIe, AGP, etc.)
Power connectors
SATA connectors for storage devices
USB ports
Integrated graphics or audio chipsets (in some cases)
What are the functions of the motherboard?
The following are the functions of the motherboard:
Performance enhancement
Communication hub
Power distribution optimization
Resource conservation
Data flow management
The following are the functions of the motherboard:
Data flow management
Performance enhancement
Communication hub
Power distribution optimization
Resource conservation
What is the difference between a CPU and a motherboard?
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is known as the brain of the computer. It processes the data by carrying out all the commands or instructions. The CPU handles the processing. While the motherboard holds the CPU and connects all the other parts of the computer to the CPU. IT flows the communication to make every system work together. The motherboard assists the communication.
Do you need a motherboard on a PC?
Yes, you will need a motherboard on your PC for effective communication between all the components. This works best for memory and CPU and maintains your storage devices. Without a motherboard, it won’t be possible for all the parts of your PC to work together.
How do motherboards work?
Motherboards connect various components via physical slots and traces on the PCB (printed circuit board). They provide power through connectors and ensure data is transferred efficiently between the CPU, RAM, and other peripherals, allowing your computer to function smoothly.
What Are the Different Sizes of Motherboards?
Motherboards vary in size to accommodate different types of systems and components. The most common sizes include:
AT
Standard ATX
Micro ATX
eXtended ATX
Flex ATX
Low-Profile EXtended (LPX)
BTX
Pico BTX
Mini ITX
Mini STX
Conclusion
Motherboards are an underrated part of our computers. Their function is to provide the base upon which everything else sits and ensure that all components can communicate and perform effectively. With various types available, from the classic AT to the modern Mini STX, there’s a motherboard option for every kind of user. Whether you’re going for maximum expandability, compactness, or a budget-friendly choice, knowing the differences will help you make informed decisions for your next build or upgrade.
Now that we’ve covered a lot about motherboards, let’s tackle some of those FAQs you might have floating around in your mind!